Comprehensive Guide to Myofascial Pain Syndrome of the Thoracic Spine

Myofascial pain syndrome of the thoracic spine is a complex chronic pain condition that significantly impacts the quality of life for those affected. In this in-depth article, we will explore its definitions, symptoms, treatment options, and the essential role it plays within the broader context of health and medical care. Our goal is to provide valuable insights that can help individuals and healthcare professionals understand this condition better.
What is Myofascial Pain Syndrome?
Myofascial Pain Syndrome (MPS) is characterized by the presence of myofascial trigger points, which are hyperirritable spots in a taut band of skeletal muscle. These trigger points can cause not only localized pain but also referred pain in seemingly unrelated areas of the body. While myofascial pain syndrome can affect any muscle group, it is prevalent in the thoracic spine, where it often results in significant discomfort and mobility issues.
The Thoracic Spine: An Overview
The thoracic spine consists of twelve vertebrae, denoted as T1 to T12, and serves as the central support structure for the ribcage. It is responsible for protecting vital organs and maintaining overall stability. Due to its anatomical complexity, the thoracic spine is particularly susceptible to various disorders, including myofascial pain syndrome.
Causes of Myofascial Pain Syndrome of Thoracic Spine
The causes of myofascial pain syndrome of the thoracic spine can be multifactorial and often relate to lifestyle choices, physical demands, and psychological stressors. Some of the most common contributors include:
- Muscle Overuse: Prolonged activities such as heavy lifting, repetitive motions, or poor ergonomic practices can lead to muscle strain.
- Sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of physical activity can weaken spinal support muscles, leading to an increased risk of developing trigger points.
- Injury: Acute injuries to the back or surrounding areas can result in muscle tension and trigger point development.
- Postural Problems: Poor body mechanics and alignment, especially in desk jobs, can contribute significantly to myofascial pain.
- Emotional Stress: Emotional factors can lead to muscle tension and exacerbation of pain symptoms.
Symptoms of Myofascial Pain Syndrome
Individuals suffering from myofascial pain syndrome of the thoracic spine may experience a variety of symptoms. Understanding these symptoms can be instrumental in seeking appropriate treatment. Symptoms commonly associated with this condition include:
- Localized Pain: A deep, aching sensation where trigger points are located, often aggravated by movement or pressure.
- Referred Pain: Pain that radiates away from the trigger point, often felt in the arms, shoulders, neck, or even abdomen.
- Muscle Stiffness: Tightness in affected muscles, which can limit range of motion.
- Fatigue: Chronic pain and discomfort can lead to fatigue and decreased overall function.
- Sleep Disturbances: Chronic pain may interfere with sleep quality, leading to a cycle of pain and exhaustion.
Diagnostic Approaches
Effectively diagnosing myofascial pain syndrome of the thoracic spine involves a comprehensive evaluation where healthcare providers assess medical history, physical examination, and possibly advanced imaging techniques. Diagnosis often focuses on:
- Clinical Assessment: A thorough physical examination to identify tender points and evaluate range of motion.
- Medical History: Understanding lifestyle factors, previous injuries, and symptom patterns to form a complete picture.
- Diagnostic Tests: While imaging studies (like X-rays or MRIs) are not always necessary, they can help rule out other conditions.
Treatment Options for Myofascial Pain Syndrome of Thoracic Spine
Treating myofascial pain syndrome of the thoracic spine requires a multi-faceted approach. Treatment modalities aim to alleviate pain, restore function, and address underlying causes. Common treatment options include:
1. Physical Therapy
Physical therapy plays a fundamental role in managing myofascial pain syndrome. Techniques may include:
- Stretching and Strengthening Exercises: Tailored exercises can help alleviate muscle tightness and improve overall strength.
- Postural Awareness Training: Educating patients about proper body mechanics can prevent the development of trigger points.
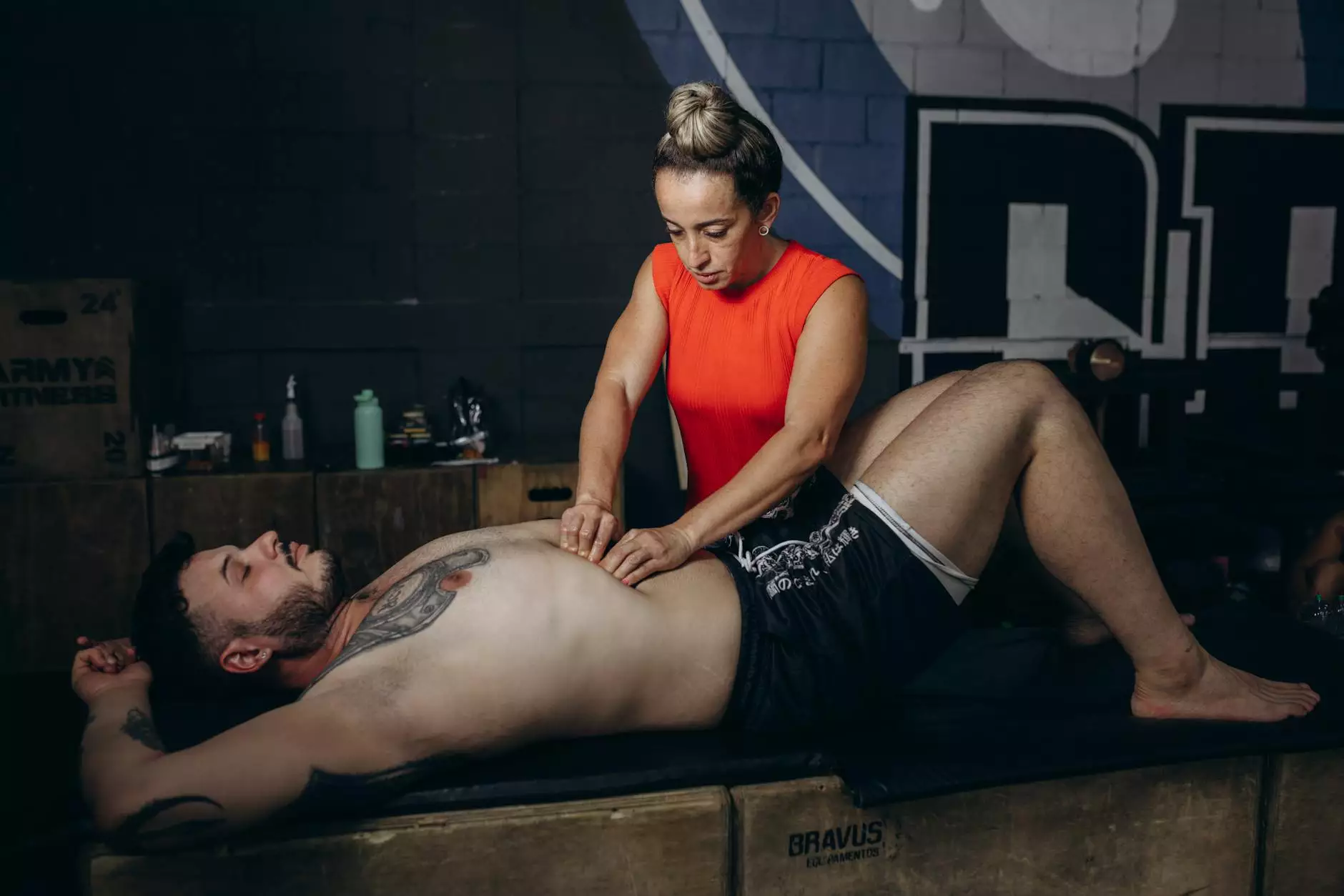
- Manual Therapy: Techniques such as massage or myofascial release can target trigger points directly.
2. Medication
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or muscle relaxants may be suggested to help manage pain and inflammation. In some cases, doctors may consider:
- Antidepressants: Low doses may improve the perception of pain.
- Topical Analgesics: Creams or patches containing pain-relieving ingredients can provide localized relief.
3. Alternative Therapies
In addition to conventional treatments, various alternative therapies may prove beneficial, such as:
- Acupuncture: Insertion of needles at specific points can stimulate healing and relieve pain.
- Chiropractic Care: Chiropractic adjustments may help realign the spine and improve function.
- Yoga and Pilates: Mind-body practices that enhance flexibility, reduce muscular tension, and promote relaxation.
Living with Myofascial Pain Syndrome
Living with myofascial pain syndrome of the thoracic spine can be challenging, but it is manageable with the right strategies. These strategies include:
- Self-Care: Engaging in regular light exercise, maintaining hydration, and practicing relaxation techniques can contribute to pain management.
- Ergonomics: Adjusting workspaces to promote better posture and reduce muscle strain.
- Support Systems: Building a support network with healthcare providers, family, and friends fosters emotional well-being and shared coping mechanisms.
The Importance of Early Intervention
Early intervention in the management of myofascial pain syndrome of the thoracic spine is crucial for successful outcomes. Delaying treatment can lead to chronic pain and further complications. If you suspect you may be experiencing symptoms related to myofascial pain syndrome, it is advisable to seek professional help promptly.
Conclusion
In conclusion, myofascial pain syndrome of the thoracic spine represents a complex, multifaceted issue that requires careful understanding and management. Through accurate diagnosis and a tailored treatment approach, individuals can achieve relief and improve their overall quality of life. Staying informed and proactive in addressing this condition is key to physical and emotional well-being.
For further resources and personalized advice tailored to your needs, consider consulting healthcare professionals specializing in pain management and rehabilitation. At IAOM-US, we provide comprehensive educational resources and support for those affected by myofascial pain syndrome and similar conditions.